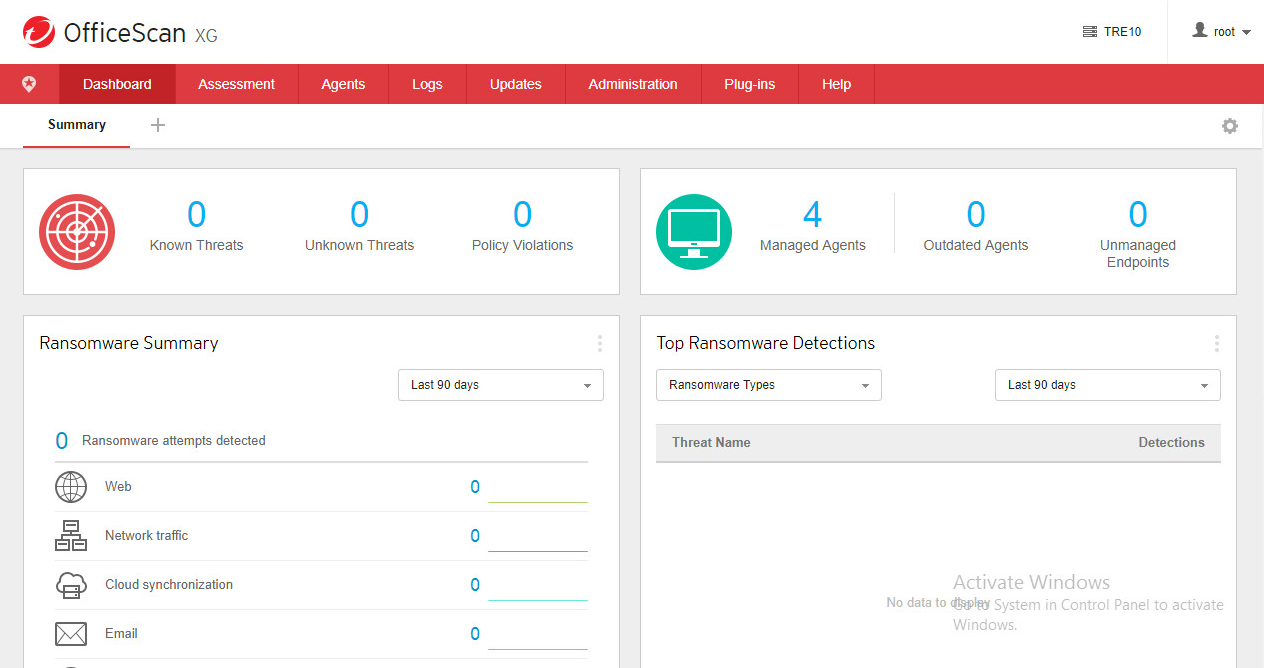
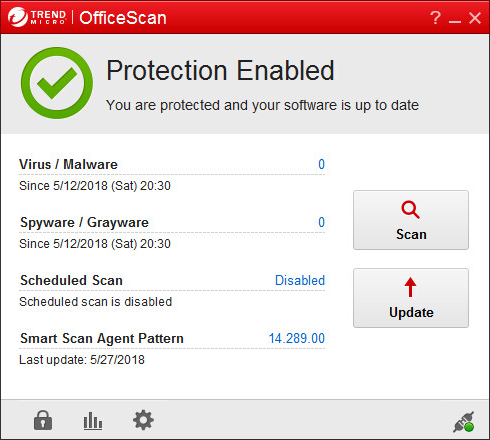
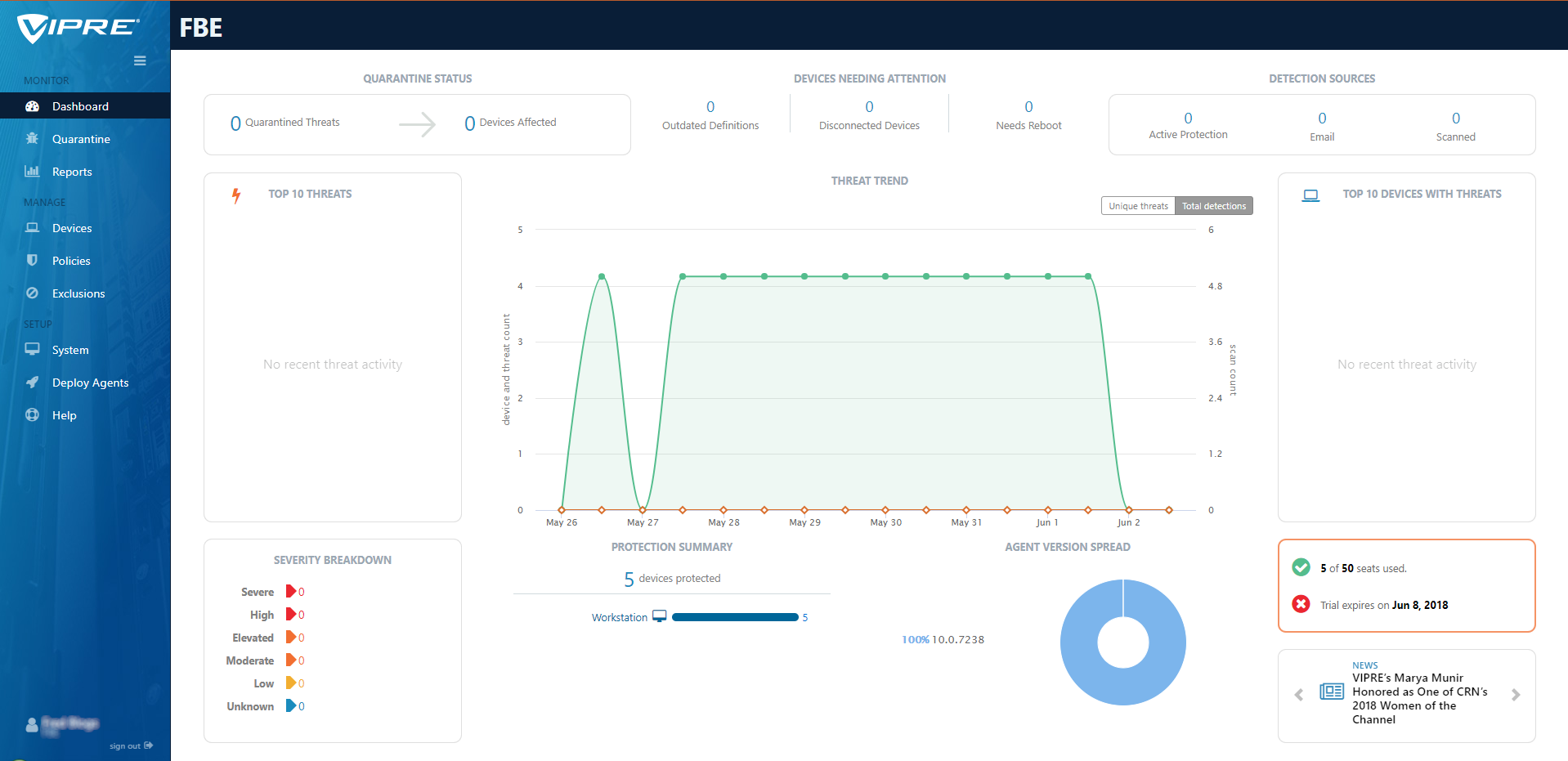
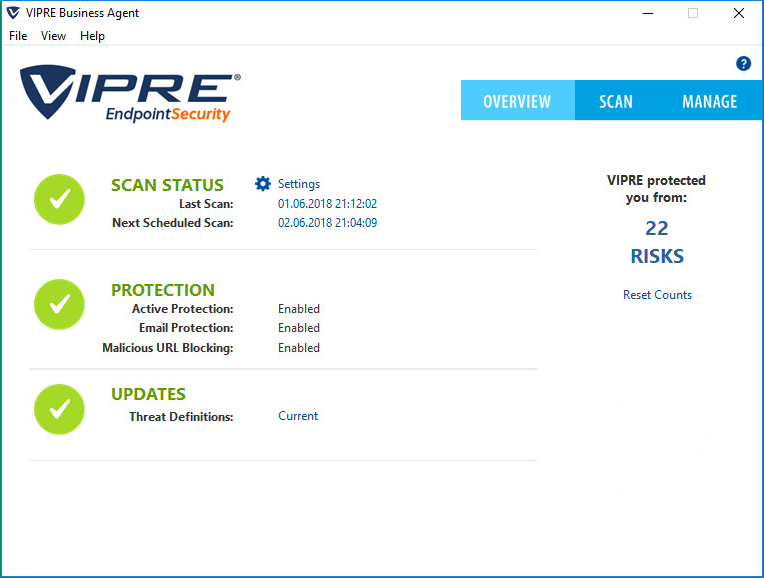
AV security software is available for all sizes and types of business. What fits well at the smaller end of the SME (small to medium enterprise) market is probably not going to be quite so appropriate to the larger corporates.
Before deciding on appropriate software to investigate, it is critical to understand the business environment in which it will be used, so that correct and informed choices can be made.
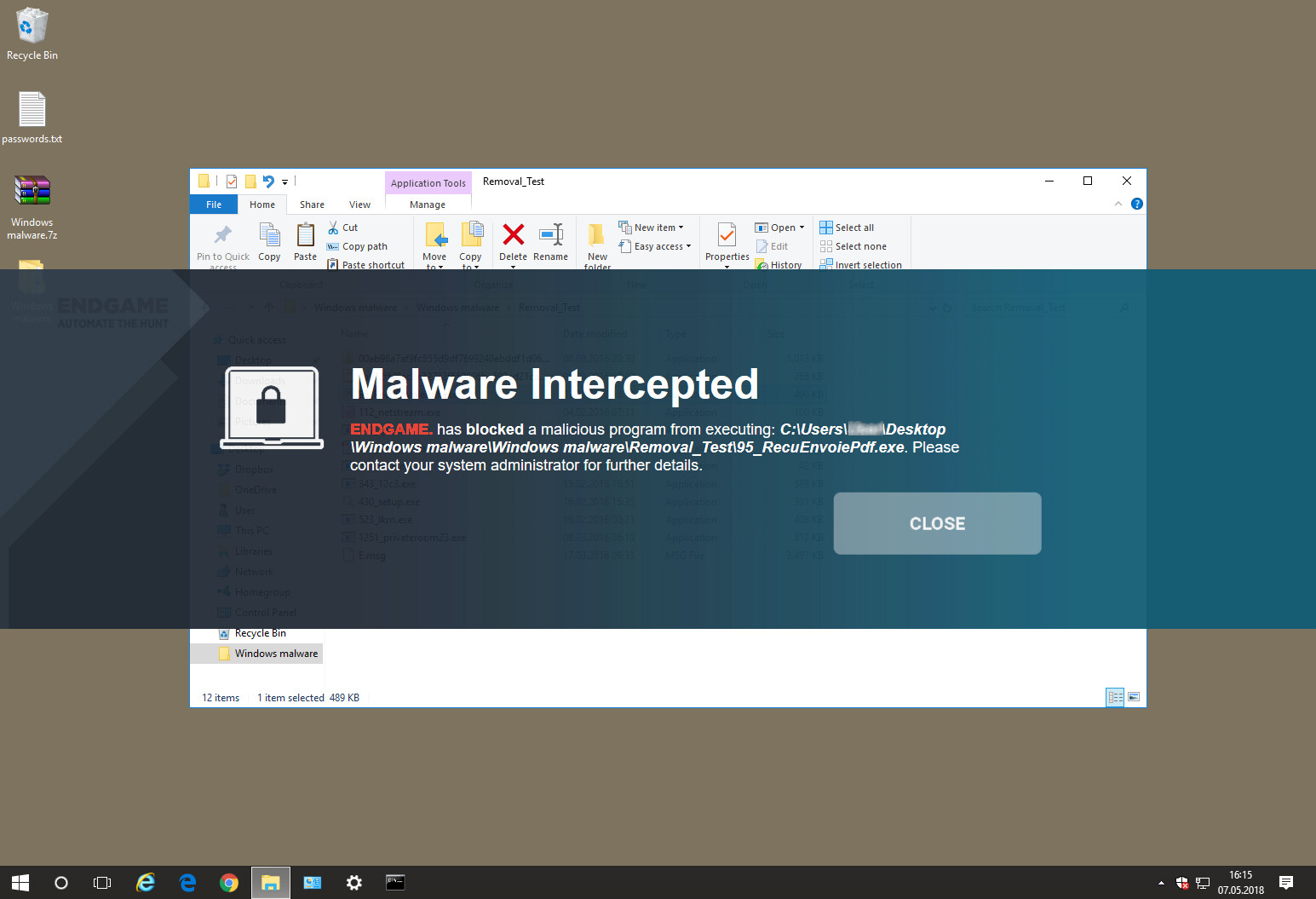
Let’s start at the smaller end of the marketplace. These are environments that have often grown out of micro businesses, where domestic-grade AV products might well have been appropriate. But as soon as you start to scale beyond a few machines, the role of AV management comes into sharp focus. This is especially true when you consider the business and reputational damage that could result from a significant, and uncontained/uncontrolled malware outbreak.
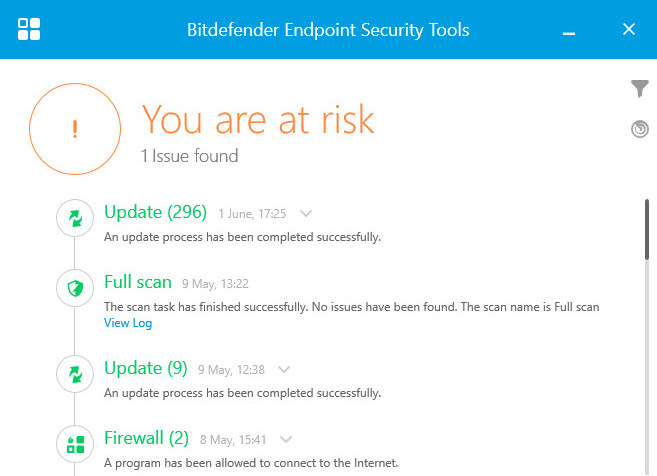
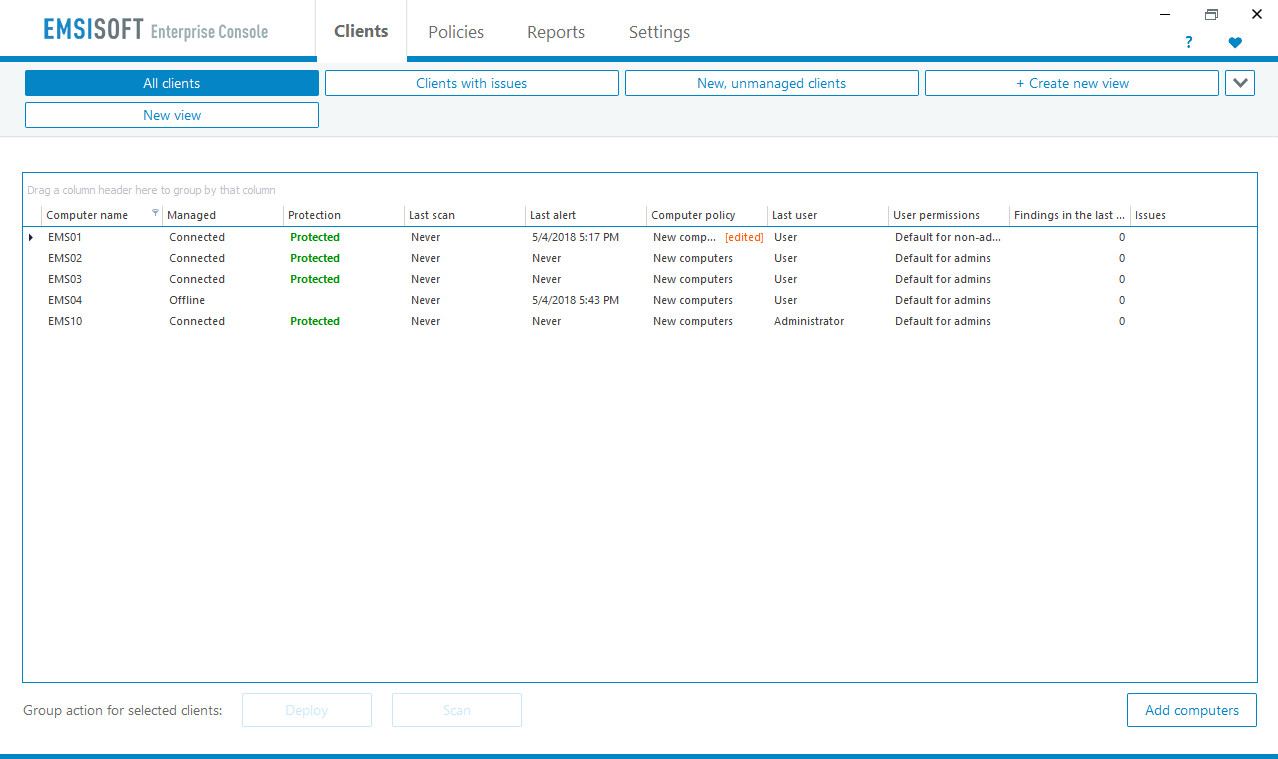
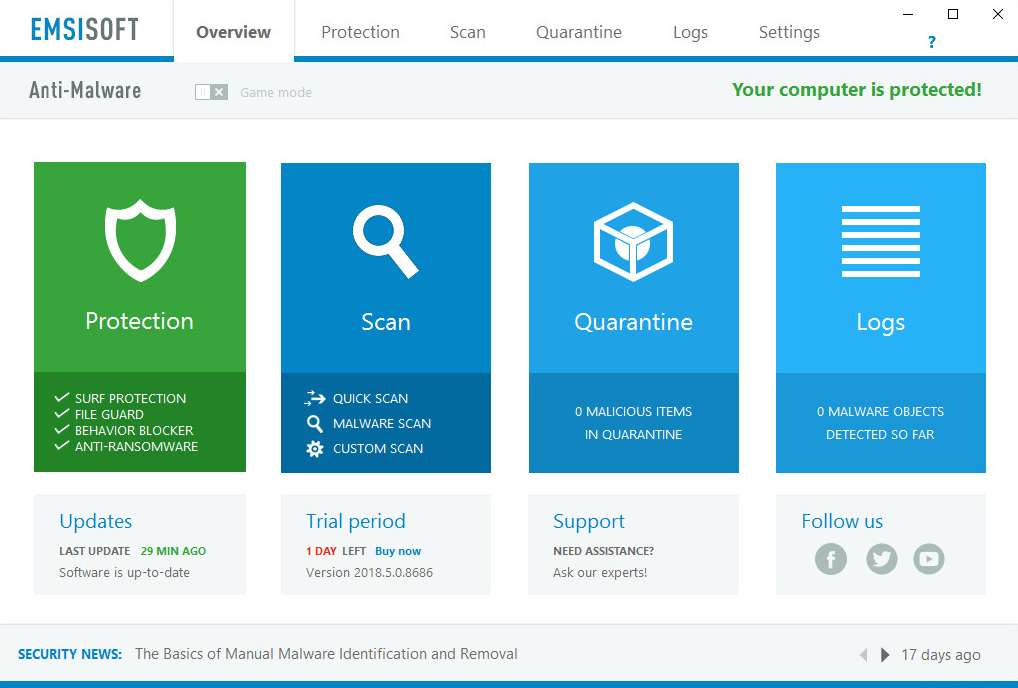
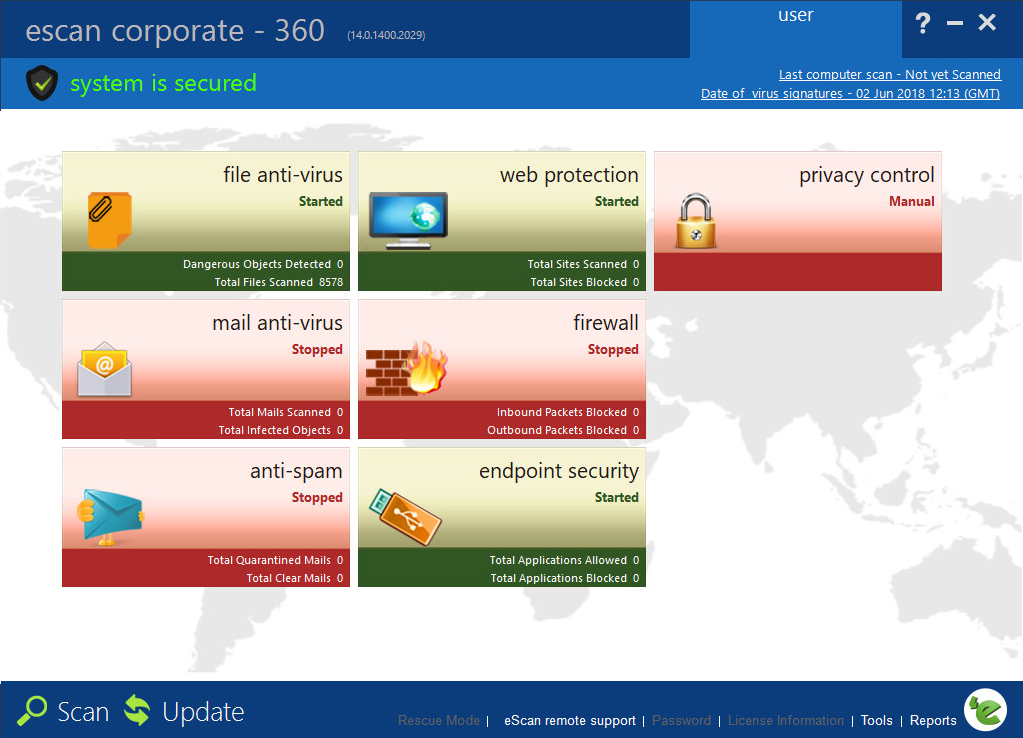
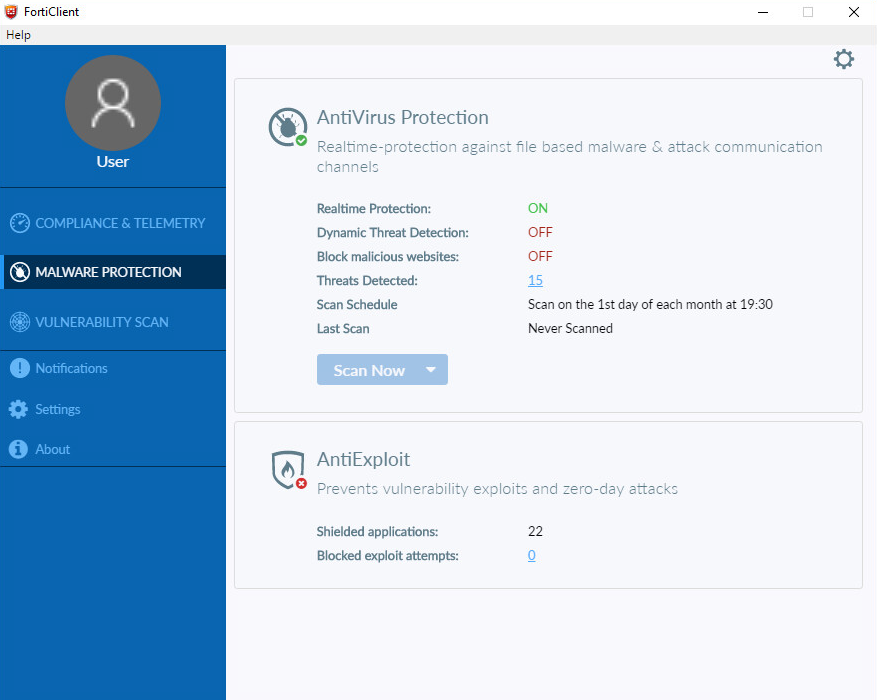
However, in the smaller end of the SME space, there is rarely an onsite IT manager or operative. Often the role of “looking after the computers” falls to an interested amateur, whose main role in the business is that of senior partner. This model is often found in retail, accountancy and legal professions. In this space, it is critical to have a managed overview of all the computing assets, and to have instant clarity about the status of the protection delivered in way that is clear and simple. Remediation can be done by taking a machine offline, moving the user to a spare device, and waiting for an IT professional to arrive on site to perform clean-up and integrity checking tasks. Although users might be informed of status, managing the platform is a task for one, or at most, a few, senior people within the organization, often driven by overriding needs for data confidentiality within the company.
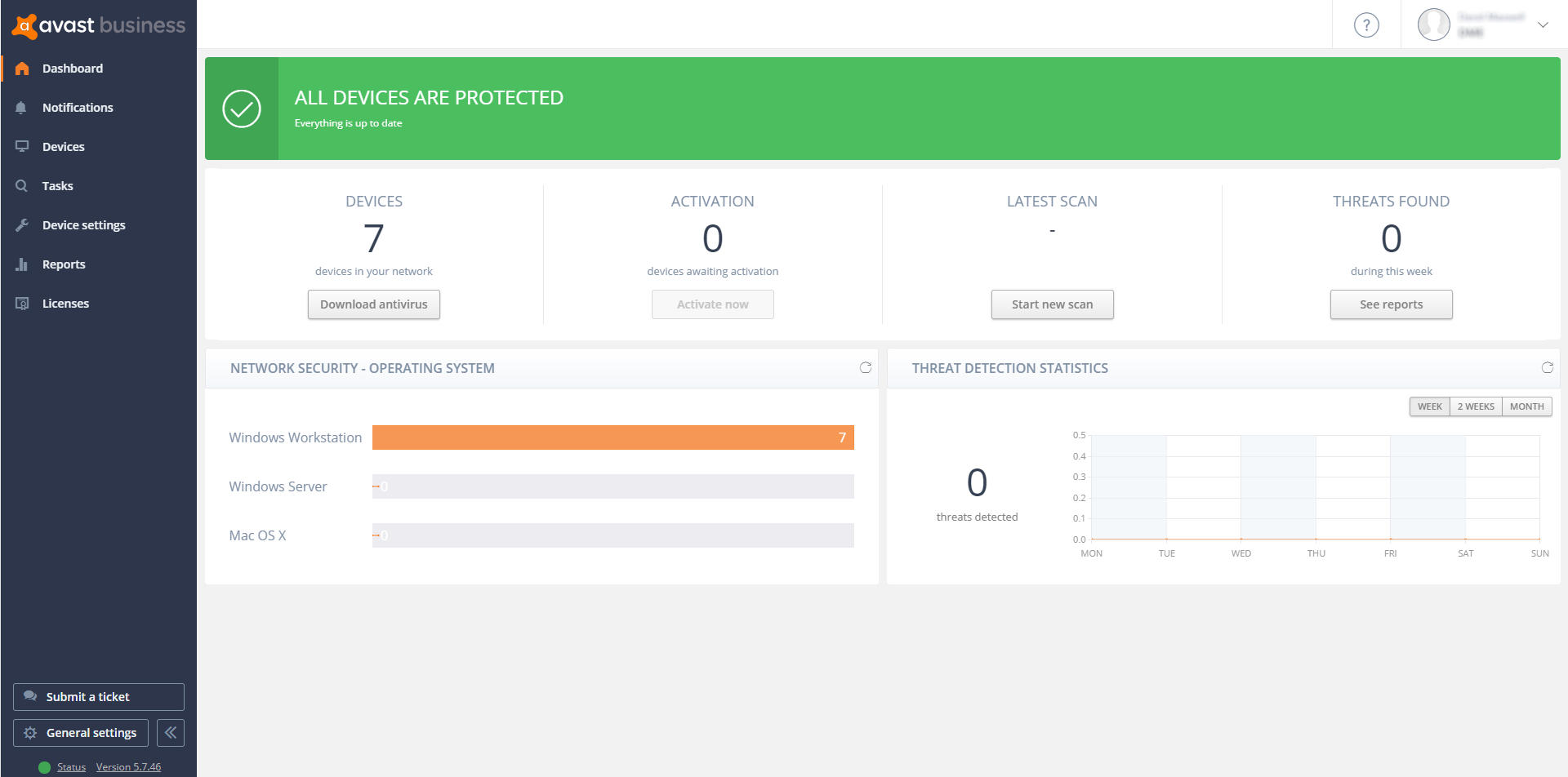
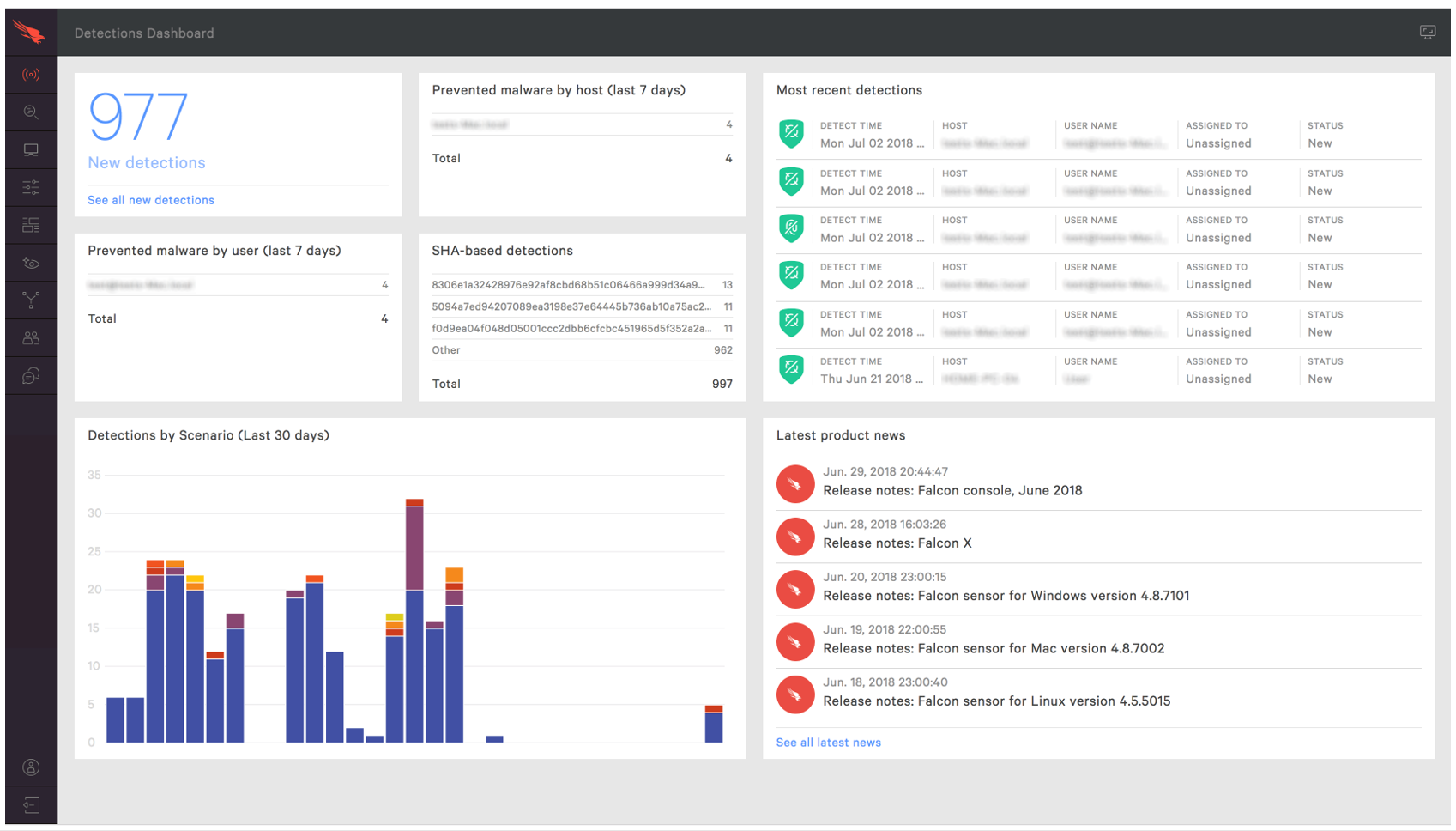
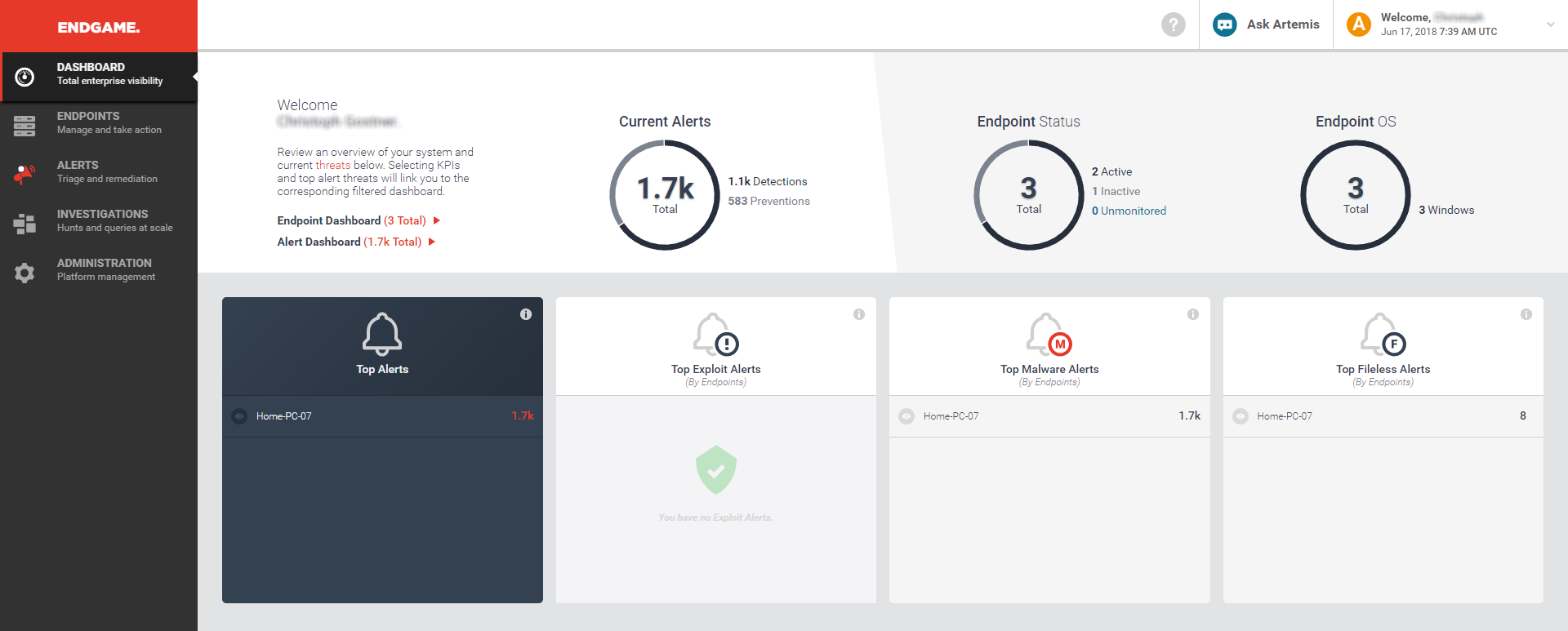
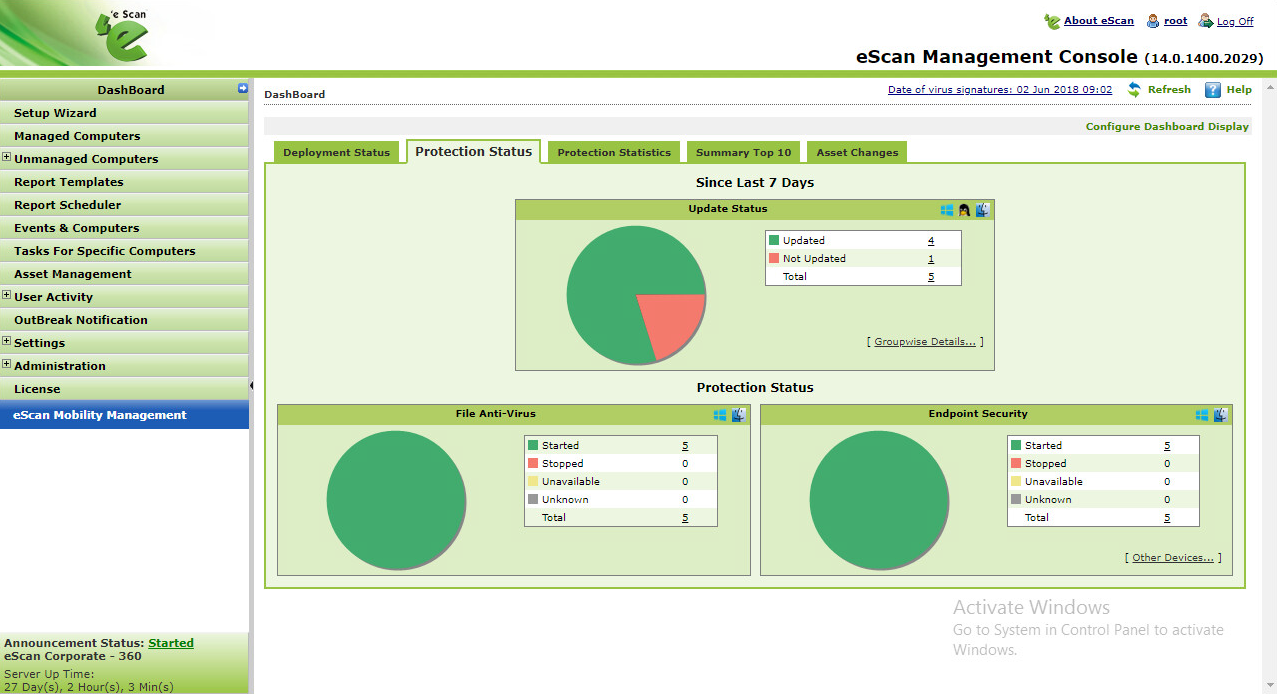
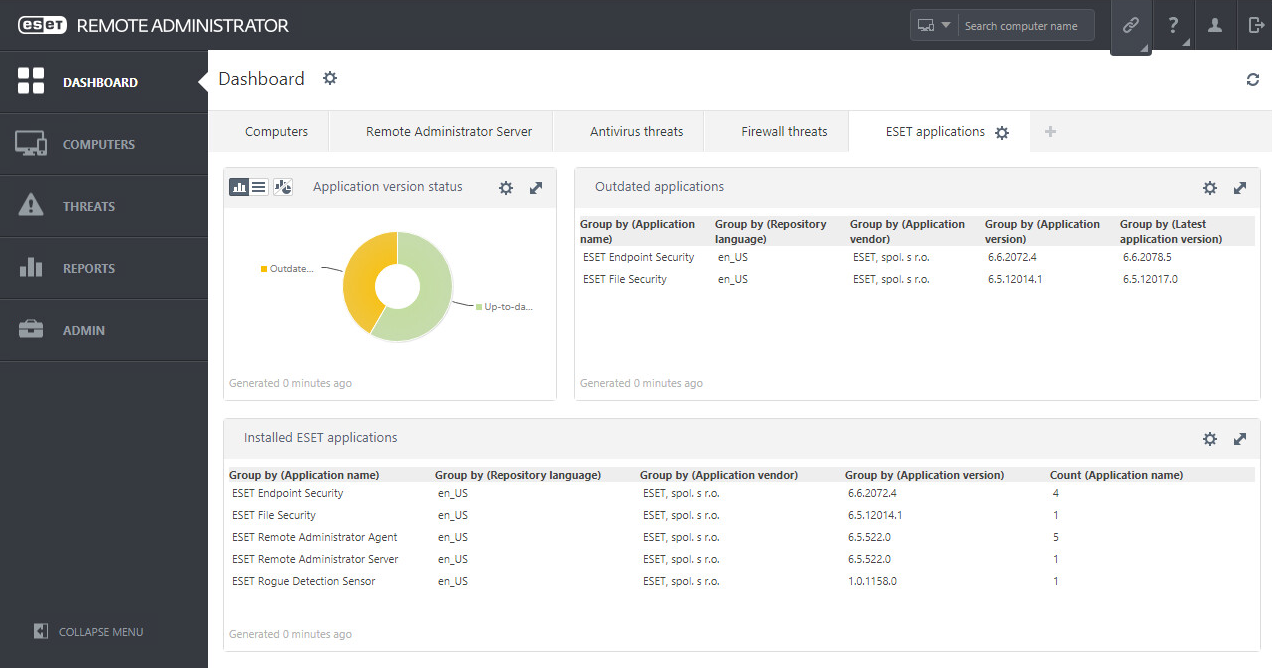
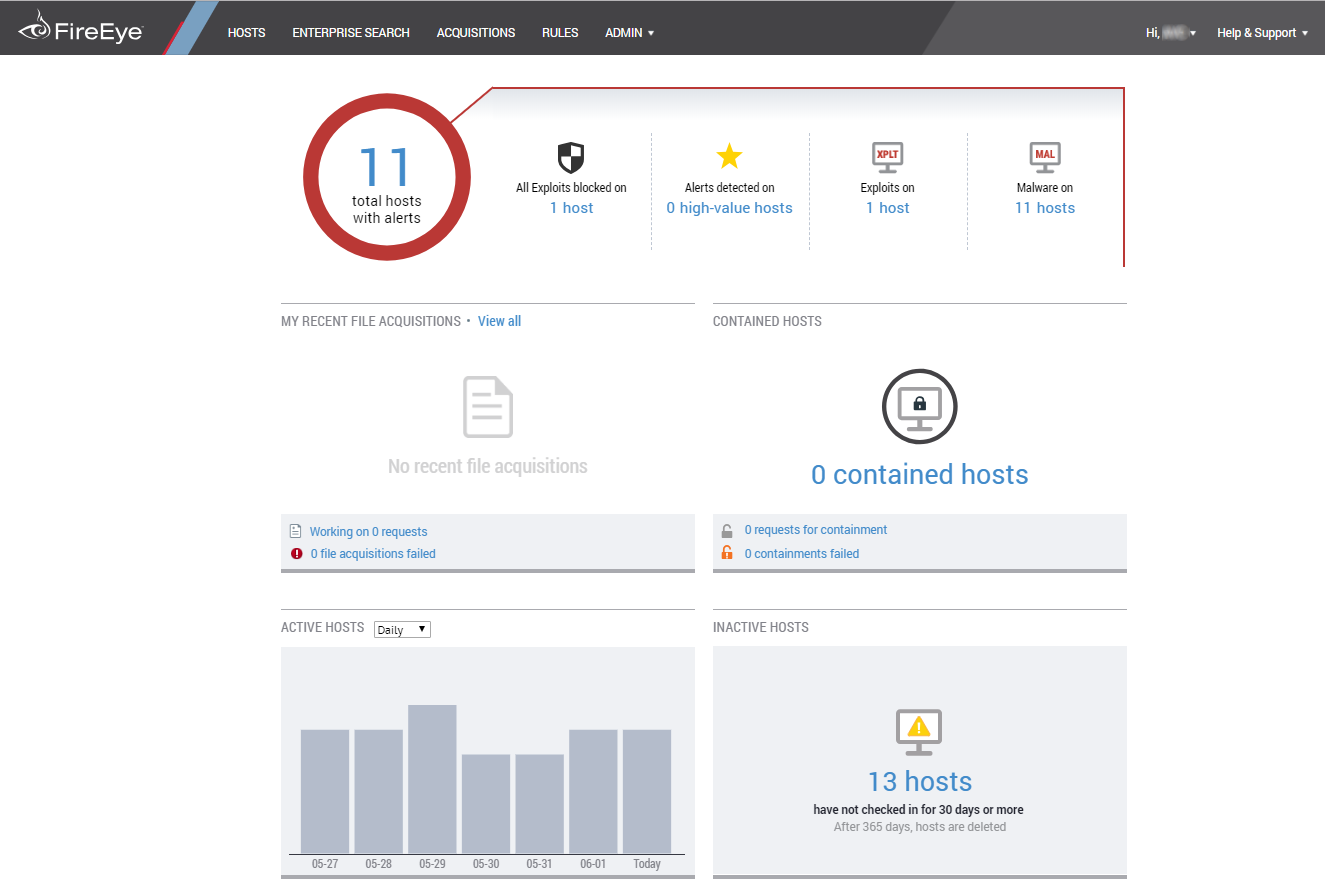
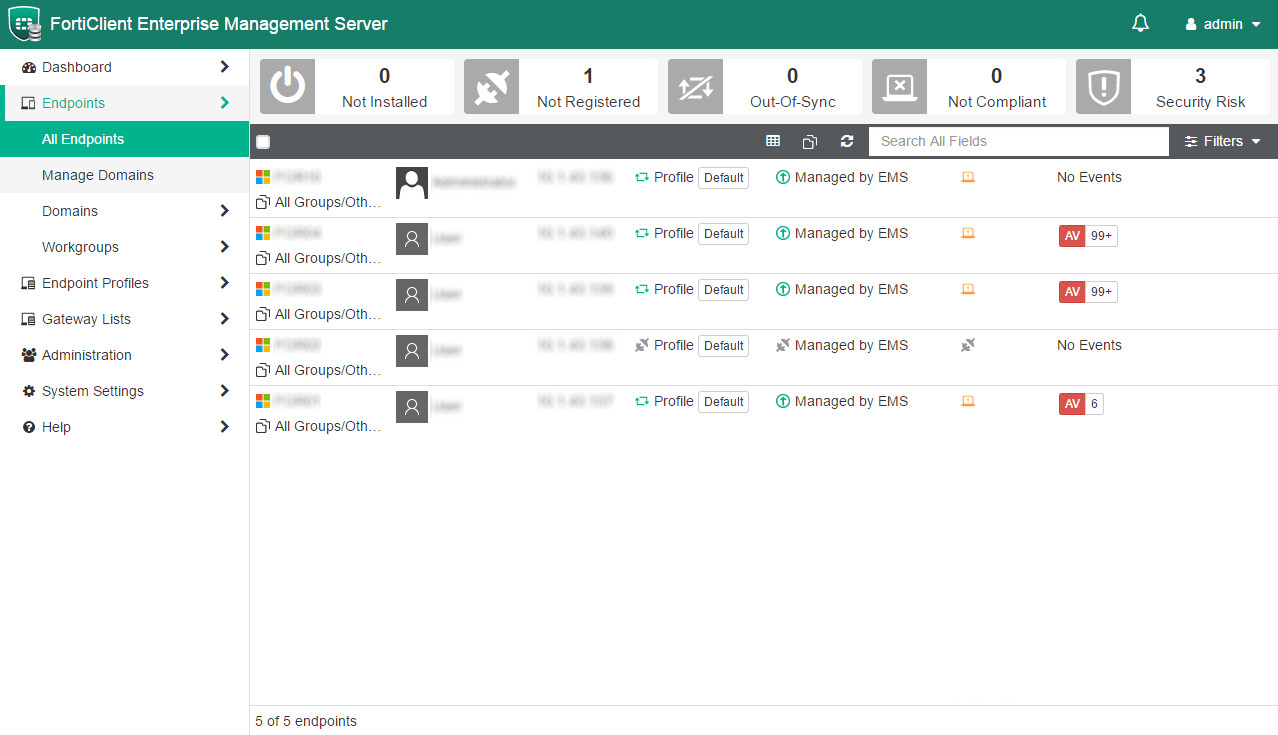
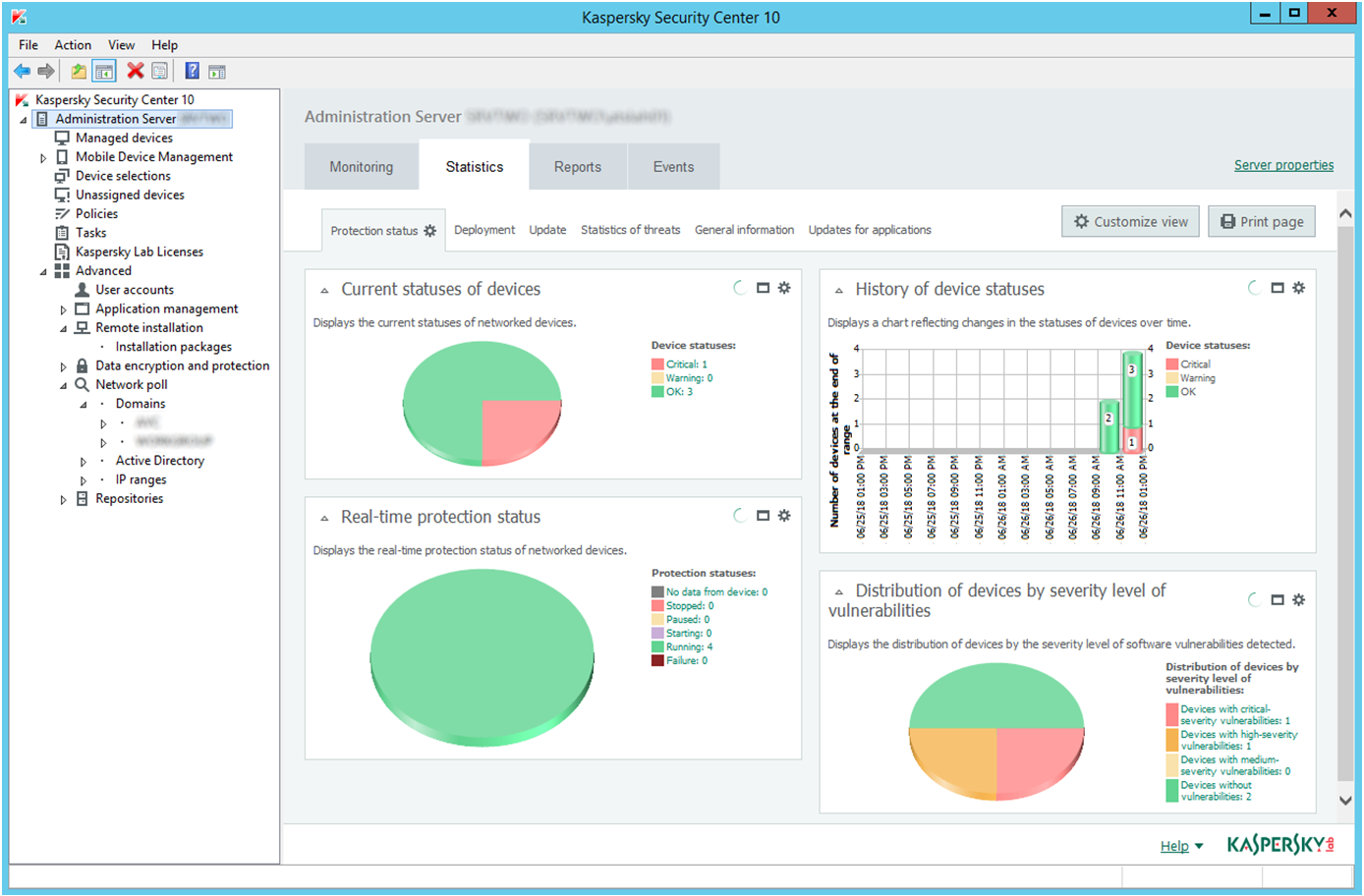
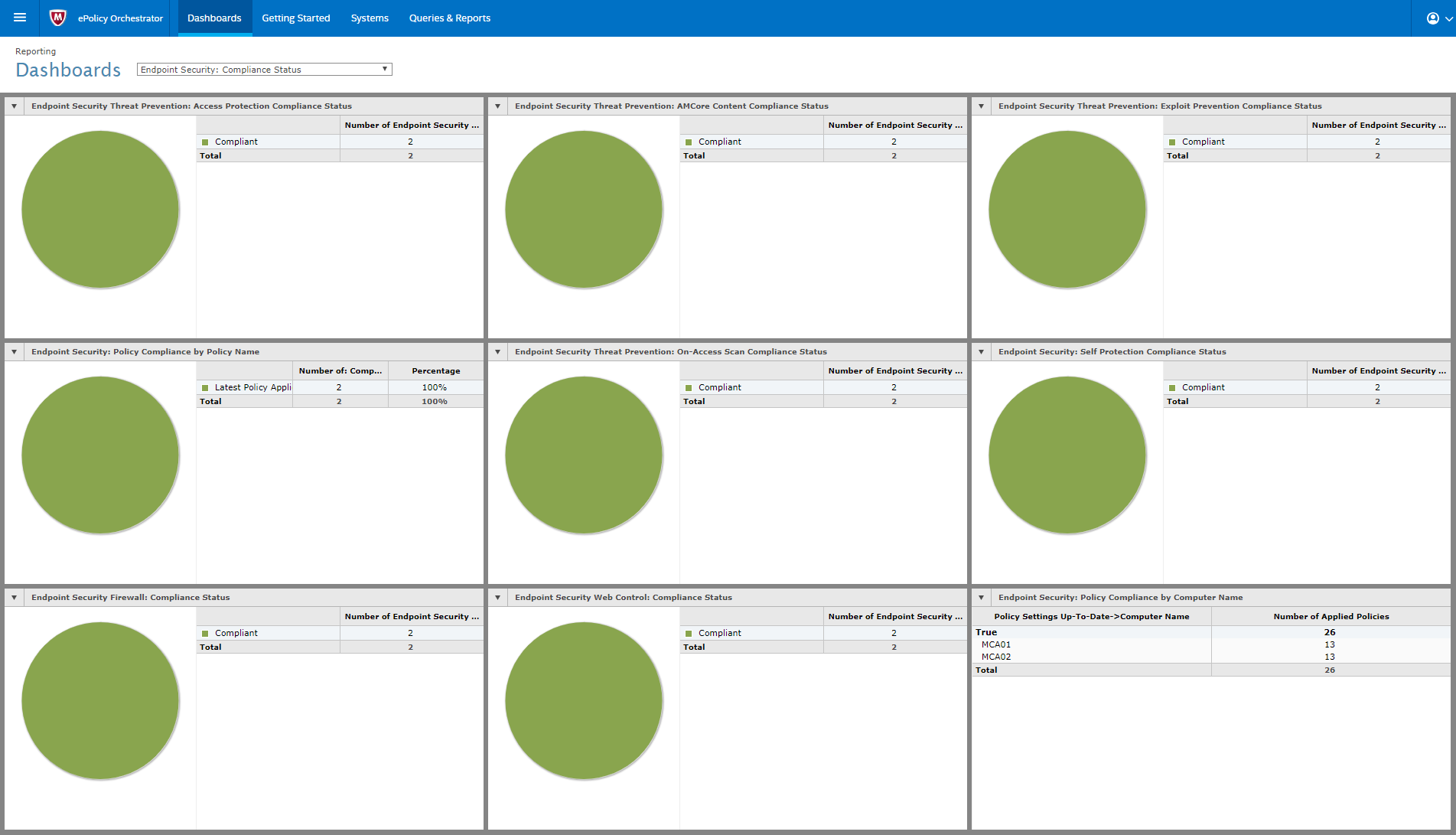
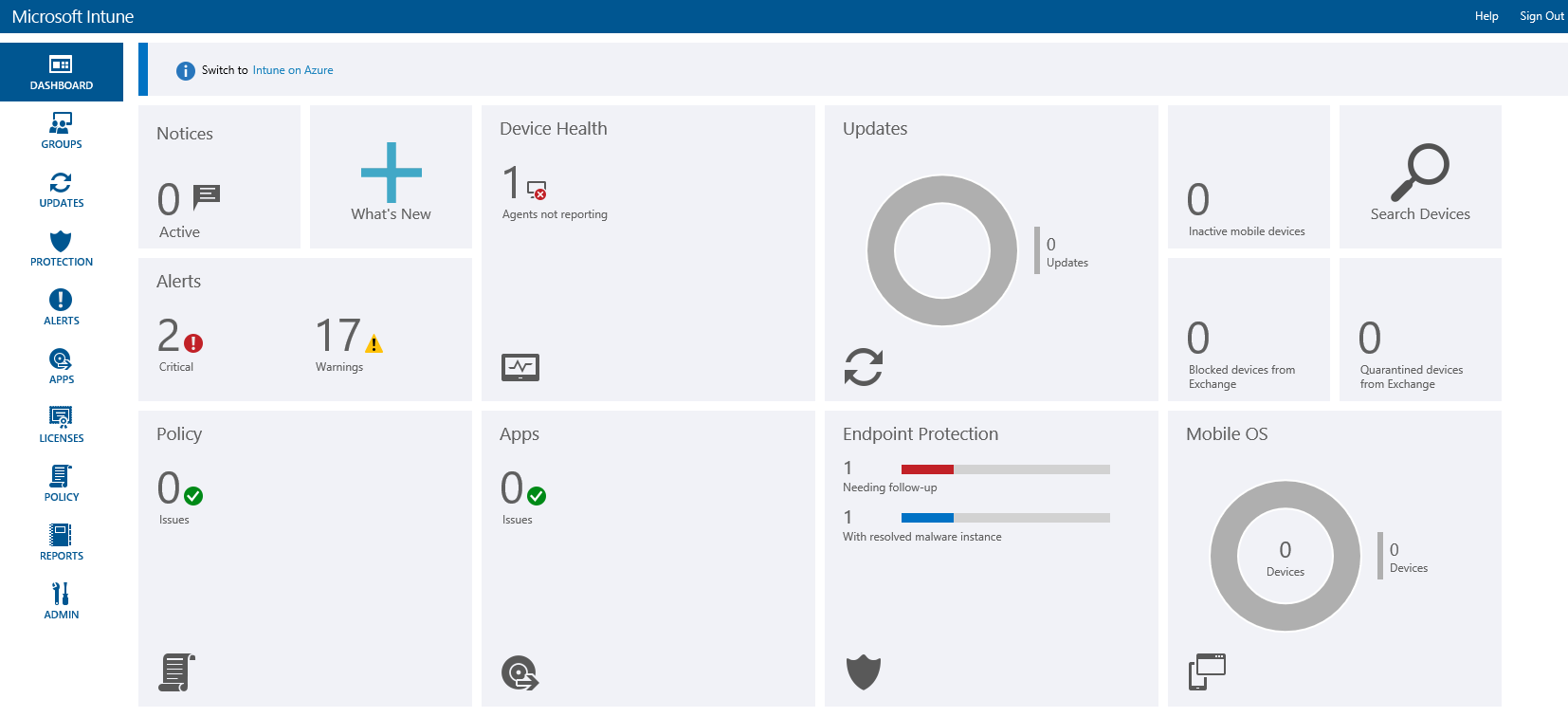
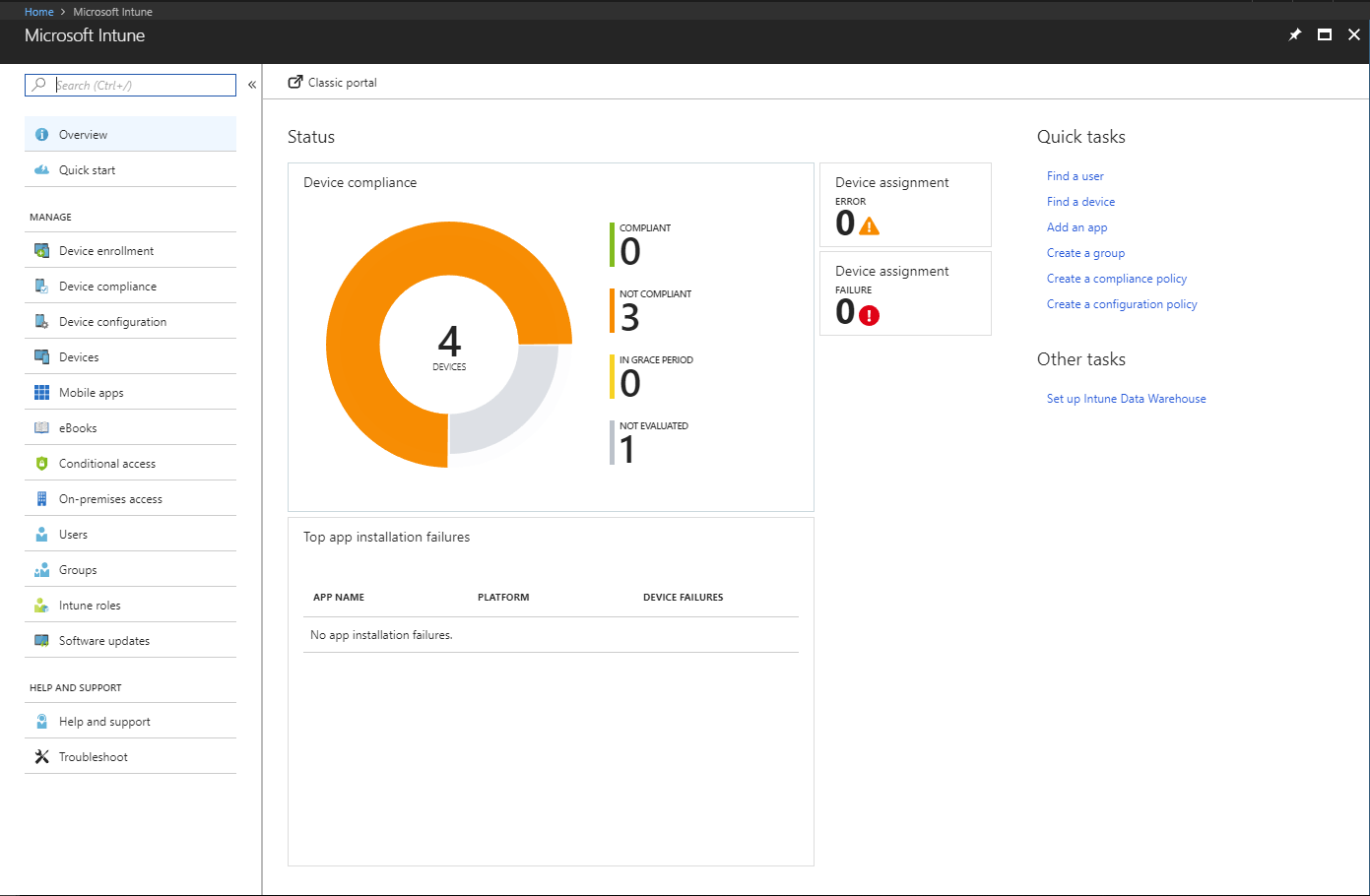
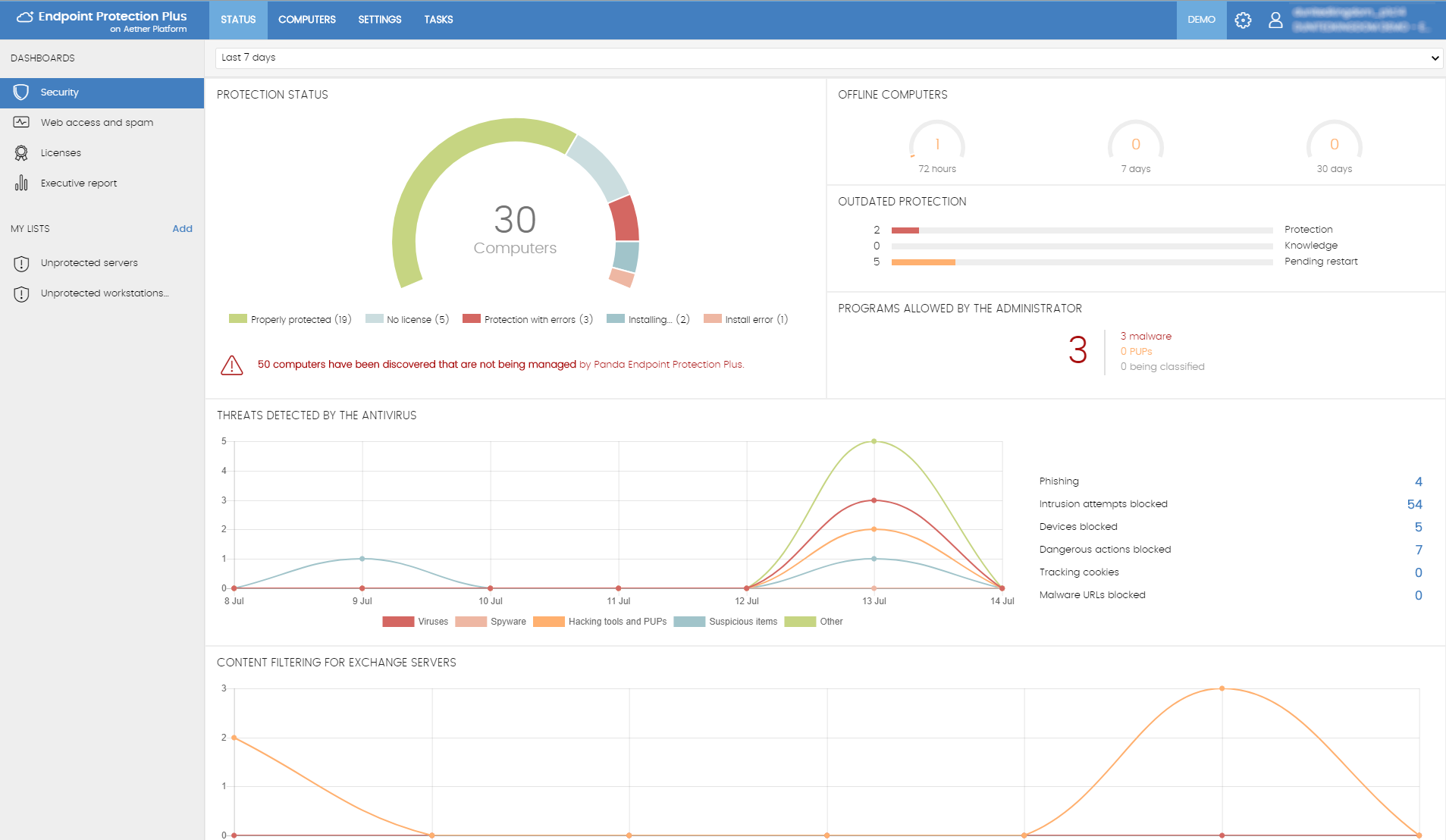
In the larger organization, it is expected to have onsite specialist IT staff, and, at the bigger end, staff whose role is explicitly that of network security. Here, the CTO role will be looking for straightforward, but real-time statistics and a management overview which allows for drilling into the data to focus on problems when they arise. There will almost be an explicit role for the software installation engineers, responsible for ensuring the AV package is correctly and appropriately loaded and deployed onto new machines. Knowing when machines “drop off grid” is almost as important here, to ensure that there are no rogue, unprotected devices on the LAN. Finally, there will almost certainly be a help desk role, as a first-line defence, who will be responsible for monitoring and tracking malware activity, and escalating it appropriately. They might, for example, initiate a wipe-and-restart on a compromised computer.
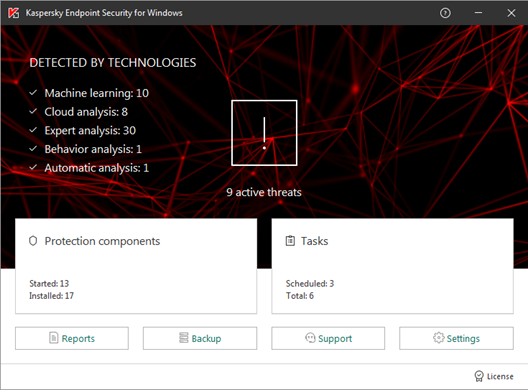
Finally, in this larger, more layered hierarchy, there is a task of remediation and tracking. Knowing that you have a malware infection is just the start. Handling it, and being able to trace its infection route back to the original point of infection, is arguably the most important function in a larger organization. If a weakness in the network security and operational procedure design cannot be clearly identified, then it is likely that such a breach will occur again at some point in the future. For this role, comprehensive analysis and forensic tools are required, with a heavy emphasis on understanding the timeline of an attack or infection from a compromised computer. Providing this information in a coherent way is not easy – it requires the handling of huge amounts of data, and the tools to filter, categorize and highlight issues as they are unfolding, often in real time.
Because of these fundamental differences, it is critically important to identify the appropriate tool for the organization, and the risk profile it is exposed to. Under-specifying this will result in breaches that will be hard to manage. Over-specifying will result in a system of such complexity that no-one truly understands how to deploy, use and maintain it, and the business is then open to attack simply because of the fog of misunderstanding and lack of compliance.
You need to make choices between going for a local-network, server-installed package, or looking at a whole cloud-based solution. There are advantages and disadvantages to both, and much will depend upon your existing infrastructure and working practices. There is no reason why one approach is inherently better than another.